10
At national scale, the National Biodiversity Strategy (Strategia Nazionale per la Biodiversità) in the
work area “Urban areas” identifies as priority green areas conservation and the requalification of the
natural areas system, to allow biodiversity and urban ecosystem protection.
Thus, urban green areas can have an important role in biodiversity conservation, both plants and
animals (especially birds, but also invertebrates, included various species of community interes
t 14).
Referring to vegetation, in cities it is possible to find monumental trees (both single tree and tree-lined
rows) and green areas of high naturalistic interest, for example forest fragments in the protected areas
of RomaNatura (Figure 2): turkey oak, hornbeam, English oak and evergreen woods in the Natural
Reserve of Insugherata; the remarkable cork oak woods in the Urban Regional Park of Pineto small
woods of turkey oak and cork oak in the Natural Reserve of Tenuta dei Massimi; oak woods and,
along the river, riparian species (elms, white willow, ashes, maples) in the Natural Reserve of Valle
dell'Aniene, etc.
Other examples are: Bosco in Città in Milan, a public park of more than 100 ha characterized by a
residual forest of Po Valley and seat of the Urban Forestry Centre; Bosco of Carpenedo in Venice, last
fragment of the ancient oakhornbeam forest that once covered Venetian inland; Bosco of Cerano and
Boschi of Santa Teresa and Lucci in Brindisi (South Italy), residuals of a coastal wood with
Mediterranean scrub and holm oak and cork oak woods.
Finally, the most natural urban green areas contribute to create ecological connections between
urban and periurban areas, representing an effective local response for safeguarding biodiversity and
protect and improve the environment.
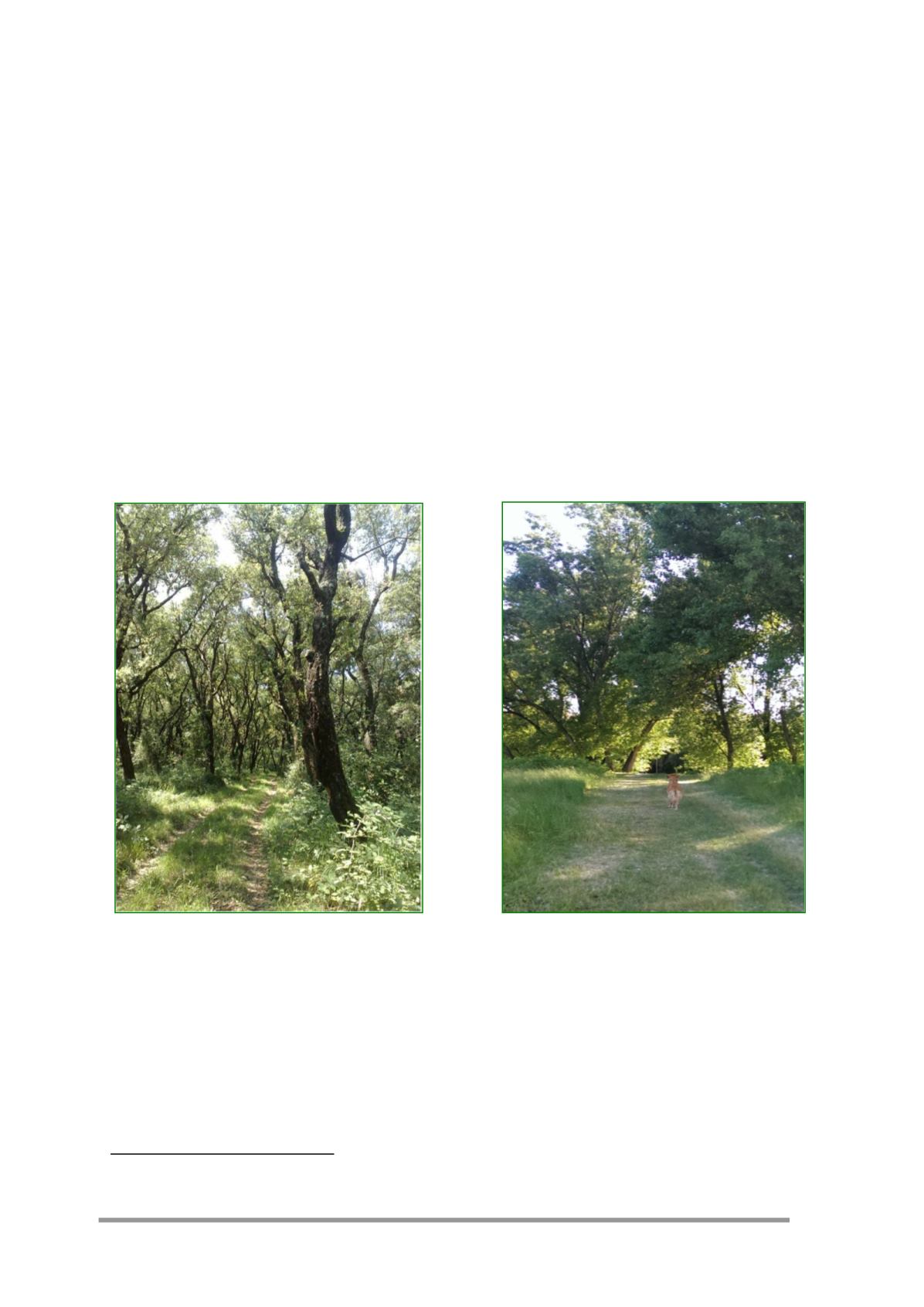
Figure 2
-
Examples of forest fragments in the protected areas of RomaNatura: cork oak woods in the Natural
Reserve of Decima Malafede (on the left) and forest fragment along the river in the Natural Reserve of Valle
dell'Aniene (on the right)
1.2 Site selection
As the main function of the new wooded area is chosen, the following step is to identify the most
suitable site where to realize the forestation intervention. A selection founded on ecological principles
allows a more successful forestry intervention, with, as well, economic benefits. In urban areas,
availability of areas where to realize forestry interventions is in general scarce (also with relation to
14
For example inside the Grande Raccordo Anulare in Rome live 5.200 insects species, included those of priority community interest (such
as
Osmoderma eremita
, discovered in Villa Borghese and Villa Pamphili, Rome) (Zapparoli, 2002.
La fauna urbana
. In: “La fauna in Italia”
(a cura di A. Minelli, C. Chemini, R. Argano, S. Ruffo), Touring Editore, Milano e Ministero dell’Ambiente e della Tutela del Territorio,
Roma).