17
Within urban “pedodiversity”, excluding soils slightly disturbed, anthropogenic soils show typical
characteristics:
−
Great vertical and spatial variability
: soil properties gradually change both spatially and
vertically. Urban soil profiles show abrupt changes from one layer to another depending upon
the human activities and the constructional history of the soil.
−
Structure Modification, compaction and organic matter decline
: compaction phenomena,
linked to trampling or vehicular traffic, with consequent reduction of water drainage, are
frequent in urban soil. The litter removal, typical in gardens or green areas, reduces organic
matter content and soil nutrients. The organic matter reduction increases water erosion,
particularly on bare soil.
−
Soil biodiversity loss
: Restricted aeration and scarce water availability caused by soil
compaction, the reduction of organic matter and diffuse soil contamination strongly
compromise soil biological quality.
−
Modified soil reaction
: soil reaction (pH) values higher than their natural counterparts are
observed in soil near the street, industries or civil buildings; the main consequence is a general
alteration of soil nutrient balances.
−
Local and diffuse contamination
: urban soil can include a high percentage of pollutants. In
addition to contamination associated with industrial activities, waste management or oil spills,
source of diffuse pollution such as vehicle traffic able to increase heavy metal concentration,
plays an important role.
Soil functions and ecosystem services change spatially and temporally with pedological
characteristics, land use and climate change. Soils provide different ecosystem services with
various quality. According to a gradient of anthropization, urban soil can be divided in four groups
(Morel et al., 2014): Vegetated pseudo-natural soil, Vegetated engineered soil, dumping sites and
sealed soil (Table 2).
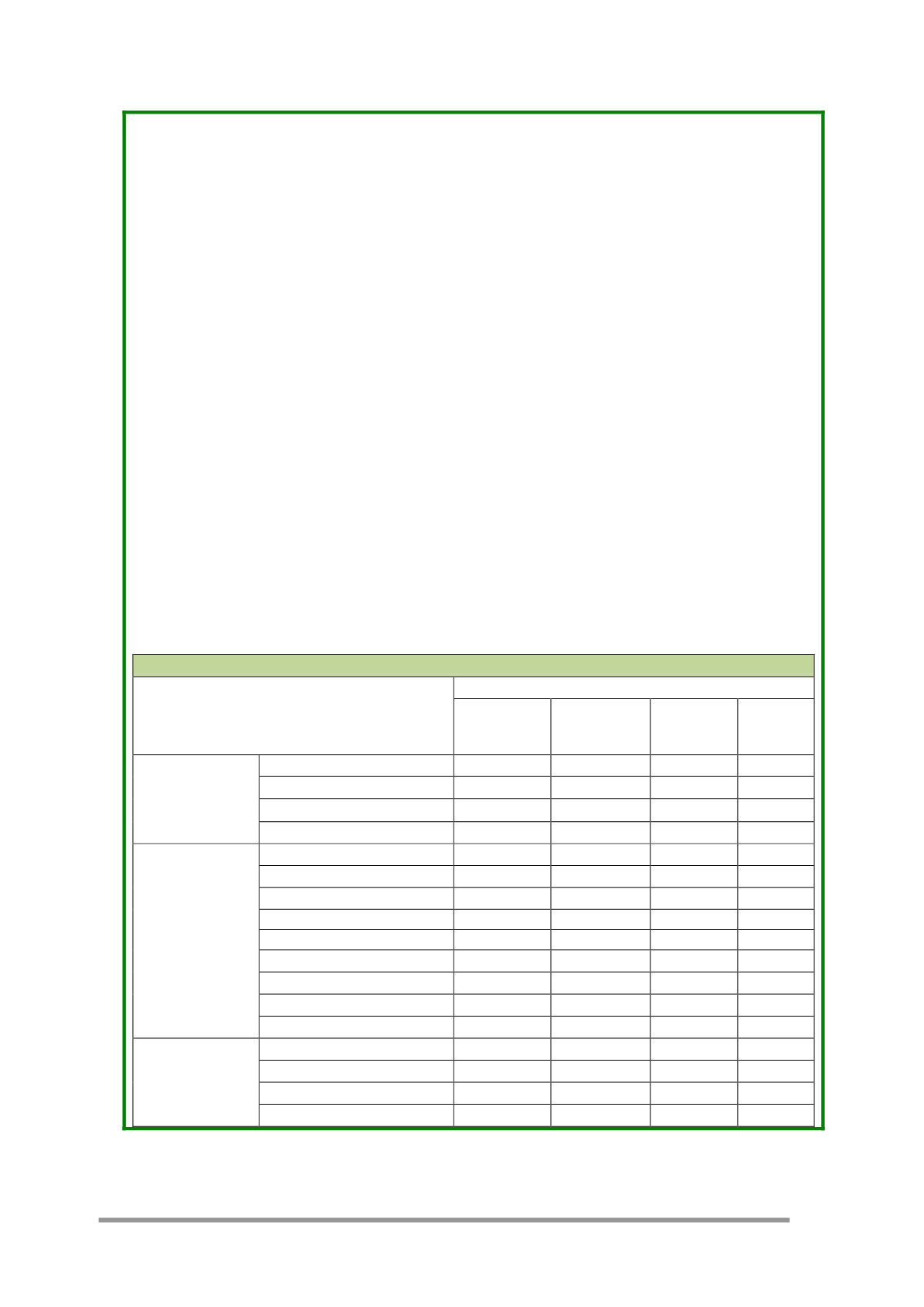
Table 2 -
Proposed categorization of urban soil based on the ecosystem services they provide.
(from Morel
Ecosystem Services
Soils
Vegetated
pseudo-natural
Vegetated
engineered
Dumping sites
Sealed
Provisioning services
Food production
++
++
(+)
o
Non-food biomass
++
++(+)
++
o
Reservoir of minerals
+
+
+++
o
Fresh water supply
o
+
o
+++
Regulating services
Water storage
++
+++
++
+
Run-off and flood control
+++
++(+)
+
+(+)
Pollution attenuation
++
+++
++
+++
Global Climate
+++
++
++
+
Local climate
+++
++
+
o
Biodiversity
+++
+++
++
o
Invasive species
o
++
o
o
Air purification
+++
++
+
o
Noise control
++
+++
++
+
Cultural services
Recreation /Tourism
+++
++
o
o
Archives of human history
+
+
+++
++
Landscape
++
+++
+
+
Education
+++
+++
++
+